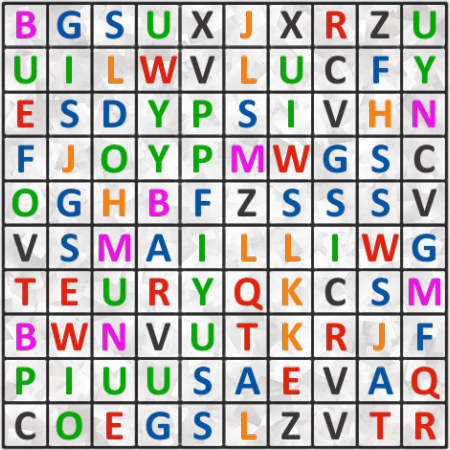
Find a famous person
Find the first and the last name of a famous person. Text may go in all 8 directions. Length of words in solution: 5,8.Correct answers: 27
The first user who solved this task is Manguexa Wagle.
#brainteasers #wordpuzzles