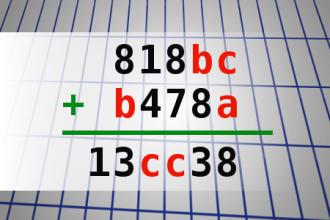
Find number abc
If 818bc + b478a = 13cc38 find number abc. Multiple solutions may exist.Correct answers: 31
The first user who solved this task is Djordje Timotijevic.
#brainteasers #math

Medication
A distraught senior citizen phoned her doctor's office. "Is it true," she wanted to know, "that the medication you prescribed To me has to be taken for the rest of my life?" There was a moment of silence before the senior lady replied, "I'm wondering, then, just how serious is my condition because this prescription is marked 'NO REFILLS'."
"Yes, I'm afraid so," the doctor told her.