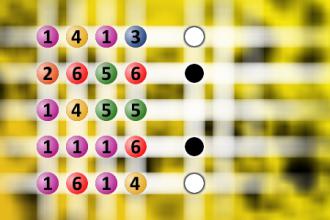
Find the right combination
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 16
The first user who solved this task is Nasrin 24 T.
#brainteasers #mastermind

A man is at the airport counter checking in his luggage...
A man is at the airport counter checking in his luggage.
The man said to the agent, "I'm flying to Los Angeles but I would like this bag to go to Portland, this one to Albuquerque, and this one to Sioux Falls."
The agent looked suitably shocked and said, "Sir, there is no way we can do that."
"Why not?", replied the man, "You did it last time".