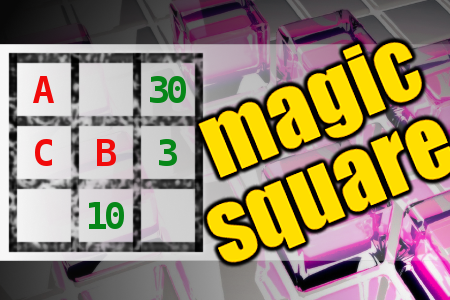
MAGIC SQUARE: Calculate A+B+C
The aim is to place the some numbers from the list (2, 3, 4, 5, 10, 12, 22, 23, 30, 47) into the empty squares and squares marked with A, B an C. Sum of each row and column should be equal. All the numbers of the magic square must be different. Find values for A, B, and C. Solution is A+B+C.
Types of Bears
A married couple was vacationing in Yosemite Park in the United States. The wife expressed her concern about camping because of bears and said she would feel more comfortable in a motel. The husband said he would like to camp outside in the woods. To calm her concerns, he suggested they talk to the park ranger to see what the likelihood of a bear encounter would be.
The ranger told them, "Well, we havewn't seen any grizzlies in this area so far this year, or black bears, for that matter."
The wife shrieked, "There are TWO types of bears out here? How can you tell the difference? Which one is more dangerous?"
The ranger replied, "Well, that's easy -- see, if the bear chases you up a tree and it comes up after you, it's a BLACK bear. If it SHAKES the tree until you fall out, it's a grizzly."
The motel room was quite nice.
Joke found on crazymady.com, posted on August 2010