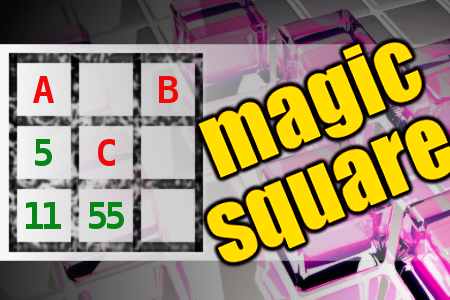
MAGIC SQUARE: Calculate A-B+C
The aim is to place the some numbers from the list (1, 2, 3, 5, 11, 12, 14, 52, 53, 55) into the empty squares and squares marked with A, B an C. Sum of each row and column should be equal. All the numbers of the magic square must be different. Find values for A, B, and C. Solution is A-B+C.Correct answers: 24
The first user who solved this task is Thinh Ddh.
#brainteasers #math #magicsquare

The Woman Is On Fire
A lady was filling her tank at a gas station, smoking a cigarette, even though all the signs say not to. The fumes that came out of the gas tank ignited, severely burning her hands.
But it also lit up her arm, too!
Instead of rolling on the ground to put it out, she panicked. She took off running down the street.
A police car was at the intersection where it happened and he tried to stop her to put out her arm, but she just kept running and screaming. All the officer could think of doing was to shoot her. This took everyone by surprise. The officer ran over to her and put the fire out, then called for an ambulance.
When questioned about his course of action to stop her, the officer said, "My only thought was to stop her. After all, she was waving a fire-arm."
But it also lit up her arm, too!
Instead of rolling on the ground to put it out, she panicked. She took off running down the street.
A police car was at the intersection where it happened and he tried to stop her to put out her arm, but she just kept running and screaming. All the officer could think of doing was to shoot her. This took everyone by surprise. The officer ran over to her and put the fire out, then called for an ambulance.
When questioned about his course of action to stop her, the officer said, "My only thought was to stop her. After all, she was waving a fire-arm."