What a winning combination?
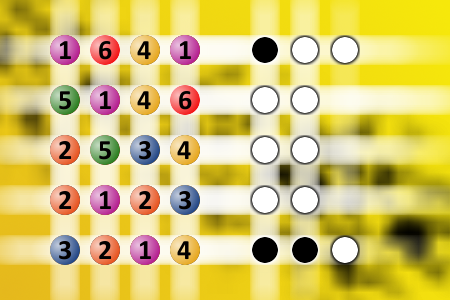
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.
200 Bucks
A guy goes over to his friends house, rings the bell.
The wife answers the door.
"Hi, is Tony home?"
"No, he went to the store."
"Well, you mind if I wait?"
"No come in."
They sit down and the friend says, "You know Sara, you have the greatest breasts I have ever seen. I'd give you a hundred bucks if I could just see one."
Sara thinks about this for a second and figures what the hell - a hundred bucks. She opens her robe and shows one. He promptly thanks her and throws a 100 bucks on the table.
They sit there a while longer and Chris says, "They are so beautiful I've got to see the both of them. I'll give you another 100 bucks if I could just see the both of them together."
Sara thinks about this and says what the hell opens her robe and gives Chris a nice long look. Chris thanks her and throws another 100 bucks on the table then says he can't wait any longer for Tony and leaves.
A while later Tony arrives home and his wife says, "You know, your weird friend Chris came over."
Tony thinks about this for a second and says, "Well, did he drop off the 200 bucks he owes me?"