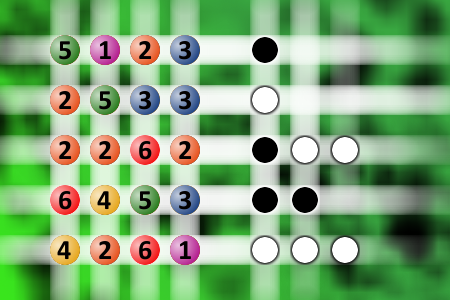
What a winning combination?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 28
The first user who solved this task is Djordje Timotijevic.
#brainteasers #mastermind

Running Out Of Fuel
My friend is notorious for waiting until the needle is on empty before filling his gas tank. Finally his car died on him, and we had to push it to the nearest filling station. After my friend finished pumping gas, the attendant asked if he had learned anything.
“Yeah,” my friend muttered, “I learned I have a 15-gallon tank.”