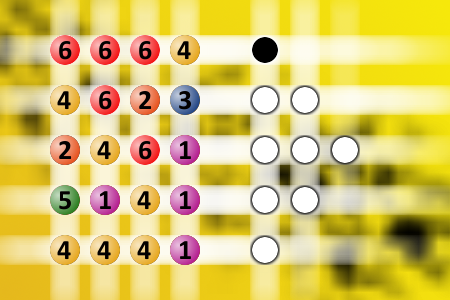
What a winning combination?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 32
The first user who solved this task is Djordje Timotijevic.
#brainteasers #mastermind

Aoccdrnig to a rscheearch at a...
Aoccdrnig to a rscheearch at an Elingsh uinervtisy, it deosn't mttaer inwaht oredr the ltteers in a wrod are, the olny iprmoetnt tihng is taht thefrist and lsat ltteer is at the rghit pclae. The rset can be a toatl msesand you can sitll raed it wouthit porbelm. Tihs is bcuseae we do not raedervey lteter by it slef but the wrod as a wlohe.
Preosllnay I tinhk its cmolpete nenosnese......
Preosllnay I tinhk its cmolpete nenosnese......