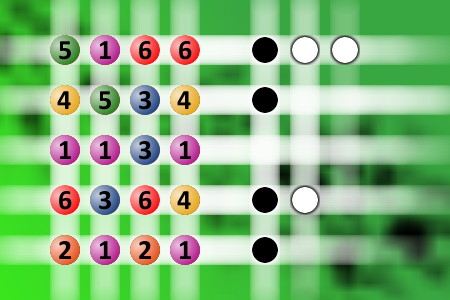
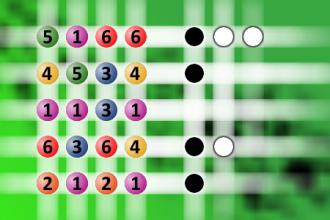
What a winning combination?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 28
The first user who solved this task is Nílton Corrêa de Sousa.
#brainteasers #mastermind

Learning From Teachers
Eight-year-old Sally brought her report card home from school. Her marks were good...mostly A's and a couple of B's.
However, her teacher had written across the bottom: "Sally is a smart little girl, but she has one fault. She talks too much in school. I have an idea I am going to try, which I think may break her of the habit."
Sally's dad signed her report card, putting a note on the back: "Please let me know if your idea works on Sally because I would like to try it out on her mother."