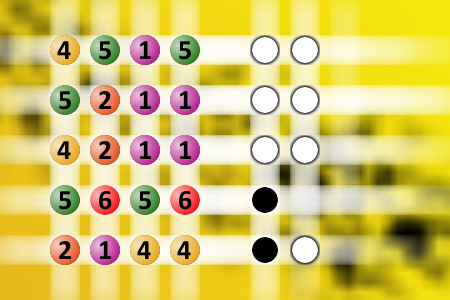
What a winning combination?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 24
The first user who solved this task is Nasrin 24 T.
#brainteasers #mastermind

Medication
A distraught senior citizen phoned her doctor's office. "Is it true," she wanted to know, "that the medication you prescribed To me has to be taken for the rest of my life?" There was a moment of silence before the senior lady replied, "I'm wondering, then, just how serious is my condition because this prescription is marked 'NO REFILLS'."
"Yes, I'm afraid so," the doctor told her.