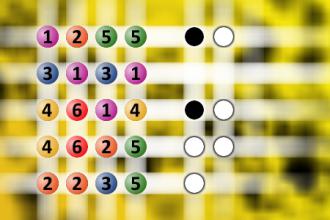
What a winning combination?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.
Earning His Stripes
A young reporter went to a retirement home to interview an aged but legendary explorer. The reporter asked the old man to tell him the most frightening experience he had ever had. The old explorer looked into the distance and warmed to his task.
“Once, I was hunting Bengal tigers in the jungles of India,” he began: “I was on a narrow path and my faithful native gun bearer was behind me. Suddenly, the largest tiger I’ve ever seen in my life leaped onto the path in front of us. I turned to get my weapon only to find my gun bearer had fled. The tiger leaped toward me with a mighty ROARRRR! I soiled myself."
“Under those circumstances, sir, I think anyone would have done the same," the reporter said.
The old explorer replied: "No, not then -– just now when I went 'ROARRRR!'”