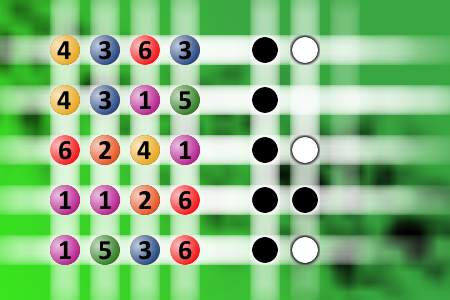
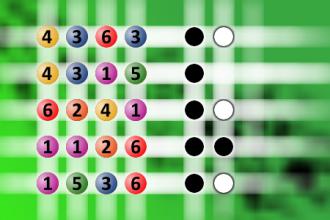
Which is a winning combination of digits?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.
Magic Window
Two guys are sitting at a bar.
"You know why I love this bar?" asks the first one.
"No," says the second guy. "Why do you love this bar?"
The first guy points at the window, which is six stories above the ground. "It has a magic window," he says. "You jump out of that window, and you can fly."
The second guy just shakes his head. "Shut up."
"No," says the first guy. "It really is a magic window. I'll prove it to you."
So the first guy gets down from his bar stool, runs at the window, jumps out of it, and flies. He flies around the building twice, up and down, and finally comes back in. He walks to his barstool, and takes a sip of his drink. "See?" he says.
The first guy looks confused. He looks at his drink. "I must be drunk," he says.
"Still don't believe me?" asks the second guy. "I'll show you again." He gets down from his stool, runs and jumps out of the window again. This time he performs some impressive aerial acrobatics, spins, flips, dives. When he finally comes back in, the second guy is staring at him, slack-jawed.
"Wow," says the second guy. "A magic window." He gets off his barstool, takes a running jump out of the window, and promptly plummets to his death. The first guy starts laughing.
The bartender comes over to the first guy with a stern look on his face. "Superman, you're a real asshole when you're drunk."