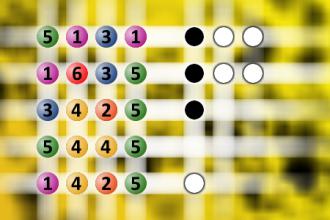
Which is a winning combination of digits?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 25
The first user who solved this task is Nasrin 24 T.
#brainteasers #mastermind

Double Martini
A businessman enters a tavern, sits down at the bar, and orders a double martini on the rocks.
After he finishes the drink, he peeks inside his shirt pocket, then orders the bartender to prepare another double martini.
After he finishes that it, he again peeks inside his shirt pocket and orders the bartender to bring another double martini. The bartender says, "Look, buddy, I'll bring ya' martinis all night long - but you gotta tell me why you look inside your shirt pocket before you order a refill."
The customer replies, "I'm peeking at a photo of my wife.
When she starts to look good, I know it's time to go home."