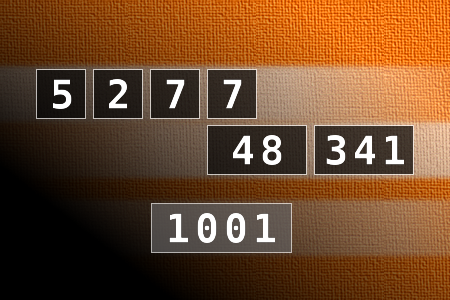Calculate the number 1001
NUMBERMANIA: Calculate the number 1001 using numbers [5, 2, 7, 7, 48, 341] and basic arithmetic operations (+, -, *, /). Each of the numbers can be used only once.
31 of the funniest jokes and best one-liners from comedians
Tim Vine Jokes and Oneliners:
1. “I’d like to start with the chimney jokes – I’ve got a stack of them. The first one is on the house.”
2. “I had a dream last night that I was cutting carrots with the Grim Reaper – dicing with death.”
3. “I saw this bloke chatting-up a cheetah. I thought: ‘He’s trying to pull a fast one.'”
4. “This bloke said to me: ‘I’m going to attack you with the neck of a guitar.’ I said: ‘Is that a fret?'”
5. “This policeman came up to me with a pencil and a piece of very thin paper. He said, ‘I want you to trace someone for me.'”
6. “Somebody actually complimented me on my driving today. They left a little note, it said ‘Parking Fine.’”
7. “Crime in multi-storey car parks. That is wrong on so many different levels.”
8. “I met this bloke with a didgeridoo and he was playing Dancing Queen on it. I thought, ‘that’s Abba-riginal.'”
9. “Uncle Ben has died. No more Mr Rice Guy.”
10. “I went to buy a watch, and the man in the shop said ‘Analogue?’ I said ‘No, just a watch.'”
11. “Exit signs? They’re on the way out!”
12. “Conjunctivitis.com – that’s a site for sore eyes.”
13. “My next door neighbour worships exhaust pipes. He’s a catholic converter.”
Milton Jones Jokes and Oneliners:
1. “Years ago I used to supply Filofaxes for the mafia. I was involved in very organised crime.”
2. “My wife – it’s difficult to say what she does. She sells seashells on the seashore.”
3. “Hard to tell if people are interested in joining my Sarcastic Club or not…”
4. “Recently I went on a ballooning holiday – I put on four stone!”
5. “You know the animal that kills the most people in the world? The Hepatitis Bee.”
6. “The pollen count, now that’s a difficult job. Especially if you’ve got hay fever.”
7. “I hate sitting in traffic, because I always get run over.”
Ken Dodd Jokes and Oneliners:
1. “I have kleptomania. But when it gets bad, I take something for it.”
2. “I told the Inland Revenue I don’t owe them a penny. I live by the seashore.”
Miscellaneous Authors:
1. "The best time to add insult to injury is when you’re signing somebody’s cast." - Demetri Martin
2. "I usually meet my girlfriend at 12:59 because I like that one-to-one time." - Tom Ward
3. "My New Year’s resolution is to get in shape. I choose round." - Sarah Millican
4. "Hedgehogs – why can’t they just share the hedge?" - Dan Antolpolski
5. "Toughest job I ever had? Selling doors, door-to-door." - Bill Bailey
6. "I went to buy some camouflage trousers the other day, but I couldn’t find any." - Tommy Cooper
7. "I was playing chess with my friend and he said, ‘Let’s make this interesting’. So we stopped playing chess." - Matt Kirshen
8. "A cement mixer collided with a prison van. Motorists are asked to be on the lookout for 16 hardened criminals." - Peter Kay
9. "Two monkeys were getting into the bath. One said: ‘Oo, oo, aah.’ The other replied:‘Put some cold in then.’" - Harry Hill