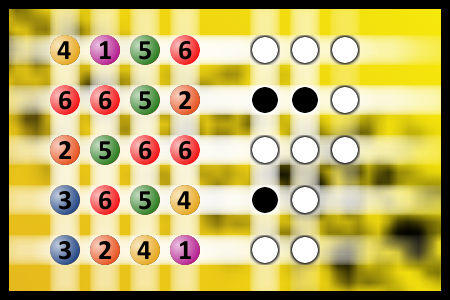
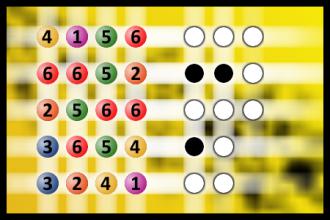
What a winning combination?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 52
The first user who solved this task is Sanja Šabović.
#brainteasers #mastermind

Twelve Days Of Fast Food
On the first day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
A Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the second day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Two Happy Meals,
and a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the third day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the fourth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the fifth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the sixth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the seventh day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Seven pints of cole slaw,
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the eighth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Eight bowls of chili,
Seven pints of cole slaw,
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the ninth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Nine polish hot dogs,
Eight bowls of chili,
Seven pints of cole slaw,
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the tenth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Ten baked potatoes,
Nine polish hot dogs,
Eight bowls of chili,
Seven pints of cole slaw,
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the eleventh day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Eleven pounds of blubber,
Ten baked potatoes,
Nine polish hot dogs,
Eight bowls of chili,
Seven pints of cole slaw,
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the twelfth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Twelve bags of Pepto,
Eleven pounds of blubber,
Ten baked potatoes,
Nine polish hot dogs,
Eight bowls of chili,
Seven pints of cole slaw,
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with Cheese
My drive through gave to me:
A Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the second day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Two Happy Meals,
and a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the third day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the fourth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the fifth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the sixth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the seventh day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Seven pints of cole slaw,
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the eighth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Eight bowls of chili,
Seven pints of cole slaw,
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the ninth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Nine polish hot dogs,
Eight bowls of chili,
Seven pints of cole slaw,
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the tenth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Ten baked potatoes,
Nine polish hot dogs,
Eight bowls of chili,
Seven pints of cole slaw,
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the eleventh day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Eleven pounds of blubber,
Ten baked potatoes,
Nine polish hot dogs,
Eight bowls of chili,
Seven pints of cole slaw,
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with cheese.
On the twelfth day of Christmas,
My drive through gave to me:
Twelve bags of Pepto,
Eleven pounds of blubber,
Ten baked potatoes,
Nine polish hot dogs,
Eight bowls of chili,
Seven pints of cole slaw,
Six chocolate milkshakes,
Five onion rings,
Four Egg McMuffins,
Three Biggie Fries,
Two Happy Meals,
And a Big Bacon Classic with Cheese