What a winning combination?
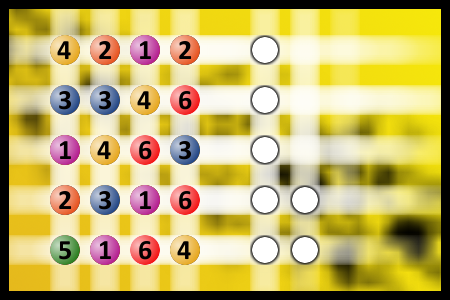
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 55
The first user who solved this task is James Lillard.
#brainteasers #mastermind

Water and Whiskey
A professor of chemistry wanted to teach his 5th grade class a lesson about the evils of liquor, so he produced an experiment that involved a glass of water, a glass of whiskey, and two worms.
"Now, class, closely observe the worms," said the professor while putting a worm into the water.
The worm in the water writhed about, happy as a worm in water could be. He then put the second worm into the whiskey. It curled up and writhed about painfully, then quickly sank to the bottom, dead as a doornail.
"Now, what lesson can we learn from this experiment?" the professor asked.
Johnny, who naturally sits in back, raised his hand and wisely, responded confidently, "Drink whiskey and you won't get worms."