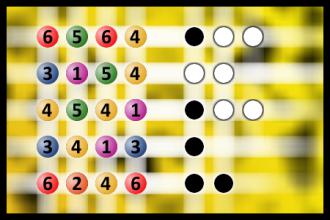
Which is a winning combination of digits?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 50
The first user who solved this task is James Lillard.
#brainteasers #mastermind

Ponderings Collection 02
If a cow laughed real hard, would milk come out her nose?
If nothing ever sticks to TEFLON, how do they make TEFLON stick to the pan?
If you tied buttered toast to the back of a cat and dropped it from a height, what would happen?
If you're in a vehicle going the speed of light, what happens when you turn on the headlights?
You know how most packages say "Open here". What is the protocol if the package says, "Open somewhere else"?
Why do they put Braille dots on the keypad of the drive-up ATM?
Why do we drive on parkways and park on driveways?
Why isn't "palindrome" spelled the same way backwards?
Why is it that when you transport something by car, it's called a shipment, but when you transport something by ship, it's called cargo?
You know that little indestructible black box that is used on planes, why can't they make the whole plane out of the same substance?
If nothing ever sticks to TEFLON, how do they make TEFLON stick to the pan?
If you tied buttered toast to the back of a cat and dropped it from a height, what would happen?
If you're in a vehicle going the speed of light, what happens when you turn on the headlights?
You know how most packages say "Open here". What is the protocol if the package says, "Open somewhere else"?
Why do they put Braille dots on the keypad of the drive-up ATM?
Why do we drive on parkways and park on driveways?
Why isn't "palindrome" spelled the same way backwards?
Why is it that when you transport something by car, it's called a shipment, but when you transport something by ship, it's called cargo?
You know that little indestructible black box that is used on planes, why can't they make the whole plane out of the same substance?