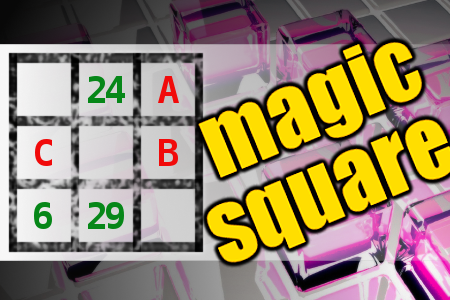
MAGIC SQUARE: Calculate A*B-C
The aim is to place the some numbers from the list (1, 4, 5, 6, 7, 22, 23, 24, 29, 30, 31) into the empty squares and squares marked with A, B an C. Sum of each row and column should be equal. All the numbers of the magic square must be different. Find values for A, B, and C. Solution is A*B-C.Correct answers: 1
#brainteasers #math #magicsquare

A man was walking along a Cali...
A man was walking along a California beach and stumbled across an old lamp. He picked it up and rubbed it and out popped a genie.
The genie said "OK, OK. You released me from the lamp... blah, blah, blah... This is the fourth time this month and I'm getting a little sick of these wishes so you can forget about three. You only get one wish!"
The man sat and thought about it for a while and said, "I've always wanted to go to Hawaii but I'm scared to fly and I get very seasick. Could you build me a bridge to Hawaii so I can drive over there to visit?"
The genie laughed and said, "That's impossible! Think of the logistics of that. How would the supports ever reach the bottom of the Pacific?
Think of how much concrete... how much steel!! No. Think of another wish."
The man said OK and tried to think of a really good wish. Finally, he said, "I've been married and divorced four times. My wives always said that I don't care and that I'm insensitive. So, I wish that I could understand women...know how they feel inside and what they're thinking when they give me the silent treatment... to know why they're crying, to know what they really want when they say 'nothing' ... to know how to make them truly happy."
The genie said, "You want that bridge two lanes or four?"
The genie said "OK, OK. You released me from the lamp... blah, blah, blah... This is the fourth time this month and I'm getting a little sick of these wishes so you can forget about three. You only get one wish!"
The man sat and thought about it for a while and said, "I've always wanted to go to Hawaii but I'm scared to fly and I get very seasick. Could you build me a bridge to Hawaii so I can drive over there to visit?"
The genie laughed and said, "That's impossible! Think of the logistics of that. How would the supports ever reach the bottom of the Pacific?
Think of how much concrete... how much steel!! No. Think of another wish."
The man said OK and tried to think of a really good wish. Finally, he said, "I've been married and divorced four times. My wives always said that I don't care and that I'm insensitive. So, I wish that I could understand women...know how they feel inside and what they're thinking when they give me the silent treatment... to know why they're crying, to know what they really want when they say 'nothing' ... to know how to make them truly happy."
The genie said, "You want that bridge two lanes or four?"