What a winning combination?
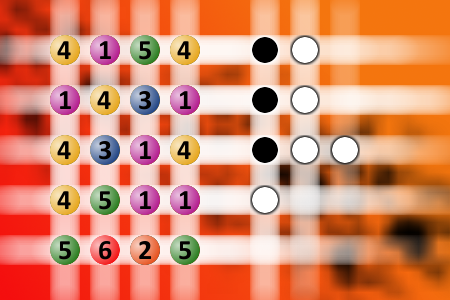
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 12
#brainteasers #mastermind

Two cows....
Two cows were chatting over the fence between their fields. The first cow said, "I tell you, this mad-cow-disease is really pretty scary. They say it is spreading fast; I heard it hit some cows down on the Johnson Farm."
The other cow replied, "Ah, I ain't worried, it won't affect us ducks."