What a winning combination?
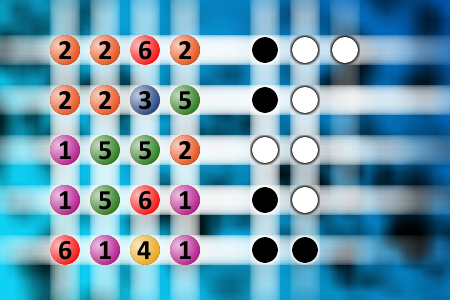
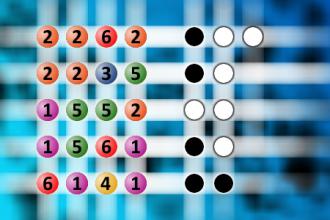
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 2
#brainteasers #mastermind

No flight ever leaves on time...
No flight ever leaves on time unless you are running late and need the delay to make the flight.
If you are running late for a flight, it will depart from the farthest gate in the terminal.
If you arrive very early for a flight, it inevitably will be delayed.
Flights never leave from Gate #1 at any terminal in the world.
If you must work on your flight, you will experience turbulence just as soon as you touch pen to paper.
If you are assigned a middle seat, you can determine who has the seats on the aisle and the window while you are still in the boarding area. Just look for the two largest passengers.
Only passengers seated in window seats ever have to get up to go to the washroom.
The crying baby on board your flight is always seated next to you.
The best-looking woman on your flight is never seated next to you.
The less carry-on luggage space available on an aircraft, the more carry-on luggage passengers will bring aboard
If you are running late for a flight, it will depart from the farthest gate in the terminal.
If you arrive very early for a flight, it inevitably will be delayed.
Flights never leave from Gate #1 at any terminal in the world.
If you must work on your flight, you will experience turbulence just as soon as you touch pen to paper.
If you are assigned a middle seat, you can determine who has the seats on the aisle and the window while you are still in the boarding area. Just look for the two largest passengers.
Only passengers seated in window seats ever have to get up to go to the washroom.
The crying baby on board your flight is always seated next to you.
The best-looking woman on your flight is never seated next to you.
The less carry-on luggage space available on an aircraft, the more carry-on luggage passengers will bring aboard