What a winning combination?
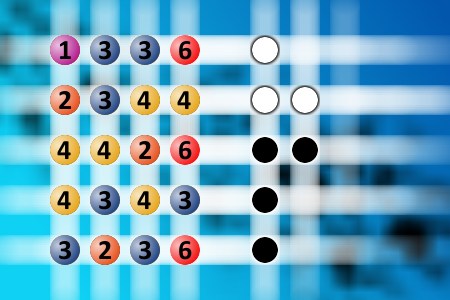
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.
Nun Sees A Naked Man
After several days of not being rescued, they agreed that they were not going to be rescued. They prayed a lot (of course), and they discussed their predicament in great depth. Finally the priest said to the nun, "you know sister, I am about to die, and there's always been one thing I've wanted here on earth--to see a woman naked. Would you mind taking off your clothes so I can look at you?"
The nun thought about his request for several seconds and then agreed to take off her clothes. As she was doing so, she remarked, "well, Father, now that I think about it, I've never seen a man naked, either. Would you mind taking off your clothes, too?"
With little hesitation, the priest also stripped. Suddenly the nun exclaimed, "Father! What is that little thing hanging between your legs?"
The priest patiently answered, "That, my child, is a gift from God. If I put it in you, it creates a new life."
"Well," responded the nun, "forget about me. Stick it in the camel!"