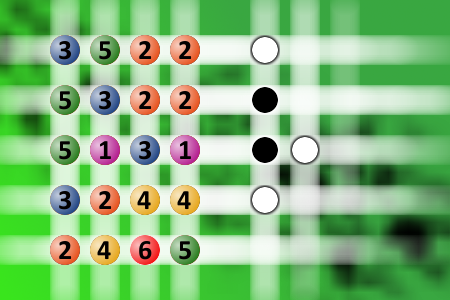
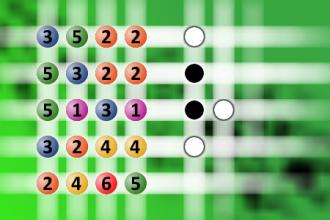
What a winning combination?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 1
#brainteasers #mastermind

A man goes to the doctors complaining of migraines and headaches
After giving the man a regular check-up and running some tests, the doctor eventually returned with three bottles. One with blue pills, one with green pills, and one with red pills.
"This is a month's supply of pills." The doctor explains. "Every morning, take one of the blue pills with a large glass of water. Every lunchtime, take one of the green pills with another large glass of water. And at bedtime take one of the red pills with another large glass of water."
Concerned with the number of pills he's going to be taking, the man asks "What's wrong with me, doctor?"
"You're not drinking enough water."