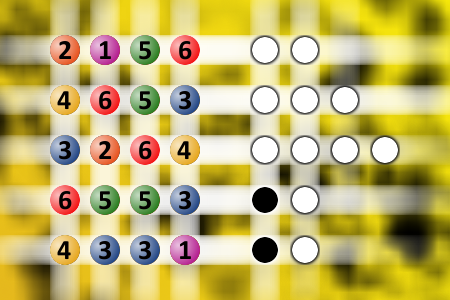
What a winning combination?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 0
#brainteasers #mastermind

Four legs
A wife comes home late one night and quietly opens the door to her bedroom.
From under the blanket, she sees four legs instead of just her husband's two.
She reaches for a baseball bat and starts hitting the blanket as hard as she can.
Once she's done, she goes to the kitchen to have a drink.
As she enters, she sees her husband there, reading a magazine.
He says, "Hi darling, your parents have come to visit us, so I let them stay in our bedroom. Did you say hello?"