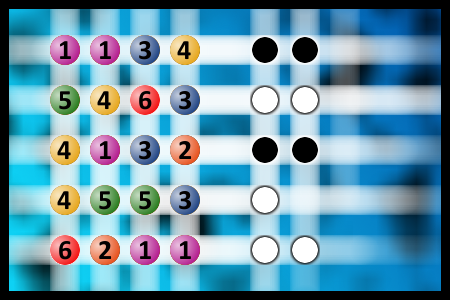
What a winning combination?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 57
The first user who solved this task is James Lillard.
#brainteasers #mastermind

Stay Over One Night
A hindu priest, rabbi and a lawyer were driving down the road, when the car breaks down. Fortunately finding a farmhouse nearby, the farmer informed them that he had only one spare room, and that it had only two twin beds.
They were welcome to it, but one of them had to sleep in the barn. After much discussion, the hindu volunteered to go to the barn. A few moments later, a knock on the bedroom door, and the hidu explained that there was a cow in the barn, and cows are sacred and he could not possibly sleep in the barn with a cow.
Annoyed, the rabbi volunteered. A few moments later, a knock on the door. The rabbi explained that there was a pig in the barn and that he, being very orthodox, could not possibly spend the evening in the barn with the origin of pork.
Finally the lawyer said that he would go to the barn. A few moments later there was a knock on the door. It was the cow and the pig!
They were welcome to it, but one of them had to sleep in the barn. After much discussion, the hindu volunteered to go to the barn. A few moments later, a knock on the bedroom door, and the hidu explained that there was a cow in the barn, and cows are sacred and he could not possibly sleep in the barn with a cow.
Annoyed, the rabbi volunteered. A few moments later, a knock on the door. The rabbi explained that there was a pig in the barn and that he, being very orthodox, could not possibly spend the evening in the barn with the origin of pork.
Finally the lawyer said that he would go to the barn. A few moments later there was a knock on the door. It was the cow and the pig!