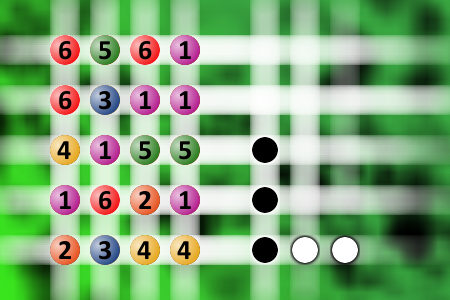
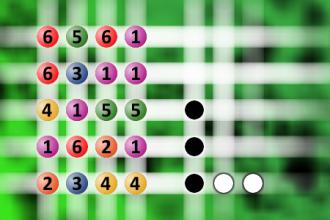
What a winning combination?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 28
The first user who solved this task is Nasrin 24 T.
#brainteasers #mastermind

Irish Marriage Jokes
Paddy was an inveterate drunkard. The priest met him one day, and gave him a strong lecture about drink.
He said, "If you continue drinking as you do, you'll gradually get smaller and smaller, and eventually you'll turn into a mouse."
This frightened the life out of Paddy. He went home that night, and said to his wife, "Bridget....if you should notice me getting smaller and smaller, will ye kill that blasted cat?"

A surgeon and an architect, both English, were joined by an Irish politician, and all fell to arguing as to whose profession was the oldest.
Said the surgeon, "Eve was made from Adam's rib, and that surely was a surgical operation."
"Maybe," said the architect, "but prior to that, order was created out of chaos, and that was an architectural job."
"Shure now," interrupted the politician, "but somebody created the chaos first."
He said, "If you continue drinking as you do, you'll gradually get smaller and smaller, and eventually you'll turn into a mouse."
This frightened the life out of Paddy. He went home that night, and said to his wife, "Bridget....if you should notice me getting smaller and smaller, will ye kill that blasted cat?"
A surgeon and an architect, both English, were joined by an Irish politician, and all fell to arguing as to whose profession was the oldest.
Said the surgeon, "Eve was made from Adam's rib, and that surely was a surgical operation."
"Maybe," said the architect, "but prior to that, order was created out of chaos, and that was an architectural job."
"Shure now," interrupted the politician, "but somebody created the chaos first."