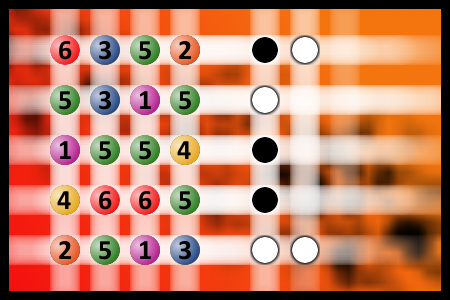
Which is a winning combination of digits?
The computer chose a secret code (sequence of 4 digits from 1 to 6). Your goal is to find that code. Black circles indicate the number of hits on the right spot. White circles indicate the number of hits on the wrong spot.Correct answers: 63
The first user who solved this task is Slobodan Strelac.
#brainteasers #mastermind

A cocky State Highways em...
A cocky State Highways employee stopped at a farm and talked with an old farmer. He told the farmer, "I need to inspect your farm for a possible new road."
The old farmer said, "OK, but don't go in that field." The Highways employee said, "I have the authority of the State Government to go where I want. See this card? I am allowed to go wherever I wish on farm land."
So the old farmer went about his farm chores.
Later, he heard loud screams and saw the State Highways employee running for the fence and close behind was the farmer's prize bull. The bull was madder than a nest full of hornets and the bull was gaining on the employee at every step!!
The old farmer called out, "Show him your card!!"