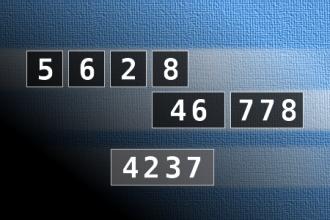
Calculate the number 4237
NUMBERMANIA: Calculate the number 4237 using numbers [5, 6, 2, 8, 46, 778] and basic arithmetic operations (+, -, *, /). Each of the numbers can be used only once.Correct answers: 0
#brainteasers #math #numbermania